Discover the benefits of sweatbands for your fitness routine. Enhance your performance and stay comfortable with these stylish and functional accessories.
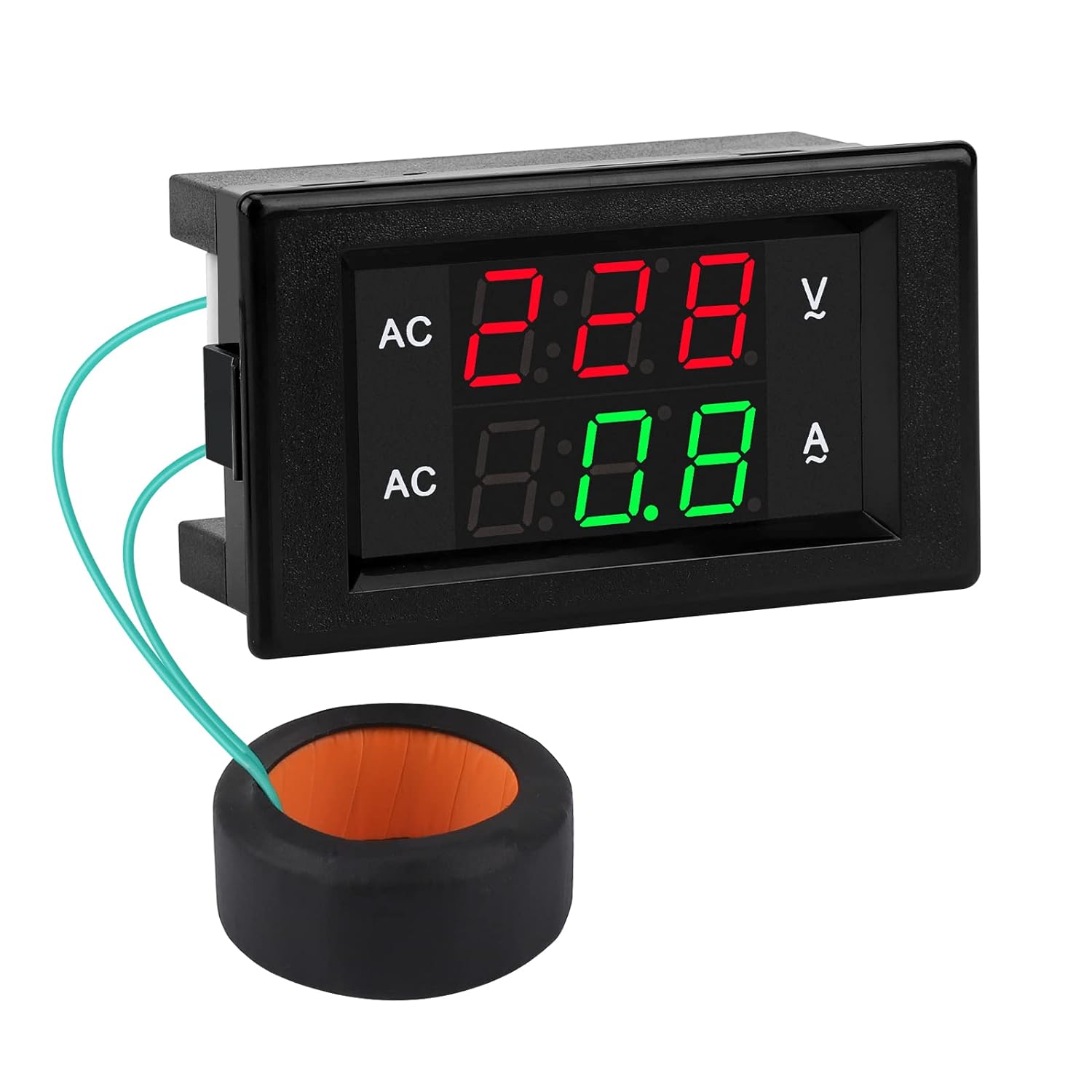


Welcome to our comprehensive guide on amp meters! In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about amp meters, also known as ammeters. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced electrician, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the world of amp meters. We will explain what amp meters are, how they work, and their various uses in different industries. So, let’s dive right in!
An amp meter, or ammeter, is a device used to measure the electric current in a circuit. It is an essential tool for electricians and technicians to ensure the proper functioning of electrical systems. Amp https://infocedia.com/electric-meter-box-power-readings/meters are designed to measure the flow of electrical current in units called amperes (A).
An amp meter works by connecting it in series with the circuit being measured. It essentially becomes a part of the circuit and measures the current passing through it. The meter has a low resistance, allowing it to accurately measure the current without significantly affecting the circuit.
When the current passes through the amp meter, it creates a magnetic field that deflects a pointer or moves a digital display. The position of the pointer or the value shown on the display indicates the amount of current flowing through the circuit.
There are several types of meters available in the market, each with its own specific features and uses. Let’s take a look at some of the most common types:
Analog amp meters have a traditional dial and pointer display. They are often preferred by electricians and technicians who prefer reading measurements from a dial rather than a digital display. Analog meters are reliable and provide accurate readings, but they may require occasional calibration.
Digital amp meters have a digital display that shows the current readings numerically. They are easy to read and provide precise measurements. Digital amp meters also offer additional features such as data logging, peak hold, and auto-ranging, making them versatile and convenient to use.
Clamp-on amp meters, also known as meters or current clamps, are designed to measure current without the need for direct electrical contact. They have a hinged jaw that can be clamped around a wire or cable to measure the current flowing through it. Clamp-on meters are commonly used in industrial and HVAC applications.
Panel-mount meters are designed to be mounted on control panels or electrical equipment. They provide a continuous display of the current flowing through a specific circuit or system. Panel-mount meters are commonly used in control rooms and industrial settings where real-time current monitoring is required.

Amp meters have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the common uses of amp meters:
Electricians and technicians use meters to diagnose and troubleshoot electrical issues. By measuring the current in different parts of a circuit, they can identify any abnormalities or faults that may be causing problems. Amp meters help in pinpointing the source of a problem and ensuring efficient repairs.
Amp meters are widely used in automotive and marine applications to monitor the charging and discharging of batteries. They help in determining the health of the battery and the efficiency of the charging system. meters are also used to measure the current draw of different electrical components in vehicles and boats.
In renewable energy systems such as solar panels and wind turbines, meters are used to monitor the flow of current. They help in optimizing the performance of the system and ensuring the efficient utilization of renewable energy sources.Meters also aid in identifying any issues or malfunctions in the system.
Amp meters play a crucial role in monitoring and controlling electrical currents in industrial and manufacturing processes. They are used to measure the current draw of motors, machinery, and equipment to ensure they are operating within safe limits. Meters help in preventing overloads and protecting electrical systems.
Using an amp meter correctly is essential to obtain accurate readings and ensure safety. Here are some tips for using an meter:
Before using an meter, make sure to select the appropriate range for the expected current. Using the wrong range can result in inaccurate readings or damage to the meter.
Always follow safety precautions when working with electrical systems. Ensure that the circuit is de-energized before connecting the meter. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses.
To measure the current, connect the meter in series with the circuit being measured. This means breaking the circuit and inserting the amp meter between the two ends. Ensure that the connections are secure and tight.
Read the user manual of the amp meter to understand its features, functions, and any specific instructions for use. Familiarize yourself with the controls and settings before taking measurements.
To obtain accurate readings, take multiple measurements and calculate the average. This helps in minimizing any errors or fluctuations in the current flow.

When it comes to choosing an amp meter, there are several factors you should consider. Here are some key things to keep in mind:
The accuracy of an amp meter is crucial for obtaining precise measurements. Look for a meter with a high level of accuracy, typically expressed as a percentage of the full-scale reading. For most applications, an accuracy of 1% or better is sufficient.
Consider the range of currents you will be measuring and choose an amp meter that can handle those currents. Make sure the meter has multiple ranges or is auto-ranging to accommodate a wide range of current values.
The resolution of an amp meter refers to the smallest change in current that it can detect. Higher resolution allows for more precise measurements. Look for a meter with a high resolution if you need to measure small changes in current.
Decide whether you prefer an analog or digital display. Analog displays are traditional and offer a continuous visual representation of the current. Digital displays provide numerical readings and additional features such as backlighting and data logging.
Ensure that the meter has safety features such as overload protection and fused inputs. These features protect the meter and the user from potential damage or harm in case of a current overload.
Consider any additional features that may be useful for your specific application. Some meters offer features such as peak hold, data logging, and relative measurement, which can enhance functionality and convenience.
Look for an meter that is built to withstand the demands of your work environment. Consider factors such as durability, ruggedness, and resistance to dust, moisture, and impact.
Set a budget for your amp meter purchase and choose a meter that offers the best combination of features, quality, and value within your budget. Remember that investing in a high-quality meter can save you money in the long run by providing accurate and reliable measurements.
In addition to the tips mentioned earlier, here are a few more tips to ensure accurate and safe use of an amp meter:
Before taking measurements, make sure to zero or “tare” the meter. This eliminates any residual current or offset errors and ensures accurate readings.
Do not exceed the maximum current range of the meter. Overloading the meter can cause damage and inaccurate readings. If you are unsure about the current levels, start with the highest range and work your way down to avoid overloading the meter.
Ensure that the leads are securely connected to the meter and the circuit being measured. Loose or poorly connected leads can result in inaccurate readings or damage to the meter.
Keep in mind that meters have a small resistance in their probes. This resistance can affect the current flow in the circuit being measured. For precise measurements, consider the probe resistance and compensate for it if necessary.
To maintain accuracy, consider calibrating your amp meter at regular intervals. Calibration ensures that the meter is measuring current correctly and provides reliable readings.

“I’ve been using an amp meter for several years now, and it has been an invaluable tool in my electrical work. It provides accurate readings and helps me diagnose and fix issues quickly. I highly recommend having an meter in your toolkit.” – John, Electrician
“I recently purchased a digital amp meter, and it has made my job so much easier. The digital display is clear and easy to read, and the meter has additional features like data logging that I find very useful. It’s definitely worth the investment.” – Sarah, Technician
“I’ve been using a clamp-on meter for my HVAC work, and it has been a reliable tool. While it may not provide the same level of accuracy as direct contact meters, it’s convenient and easy to use. I would recommend it for anyone in the HVAC industry.” – Mike, HVAC Technician
Yes, amp meters can measure both AC and DC currents. However, it’s important to select a meter that is designed for the type of current you are measuring.
No, amp meters are specifically designed to measure current and not voltage. To measure voltage, you would need a voltmeter.
The maximum current range of a meter depends on the specific model. Some meters can measure currents up to several thousand amperes, while others have a lower maximum range. It’s important to select an amp meter with a suitable range for your needs.
Yes, but it’s important to take proper safety precautions and ensure that you are using a meter rated for measuring live circuits. Always follow safety guidelines when working with electricity.

Amp meters are essential tools for anyone working with electrical systems. With their ability to accurately measure current and real-time monitoring capabilities, meters are indispensable for electricians, technicians, and hobbyists alike. From electrical maintenance and troubleshooting to automotive and marine applications, amp meters have a wide range of uses across various industries. It’s important to choose the right meter for your specific needs and follow safety precautions when using it. Overall, having a meter in your toolkit will greatly enhance your ability to work with electrical systems efficiently and safely.
In conclusion, amp meters are essential tools for measuring electrical currents in various applications. Whether you are an electrician, technician, or hobbyist, having a reliable meter is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. By understanding how meters work and their different types, you can choose the right meter for your specific needs. Remember to follow safety precautions and use the meter correctly to obtain accurate readings. Happy measuring!
Choosing the right meter and using it correctly is essential for accurate current measurements and the safety of electrical systems. Consider factors such as accuracy, range, resolution, and display type when selecting an amp meter. Follow the tips mentioned in this guide to ensure proper use of the meter and obtain reliable readings. With the right meter in your toolkit, you can confidently measure electrical currents and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.